Slot Blot Apparatus
A dot blot (or slot blot) is a technique in molecular biology used to detect proteins. It represents a simplification of the western blot method, with the exception that the proteins to be detected are not first separated by electrophoresis. Instead, the sample is applied directly on a membrane in a single spot, and the blotting procedure is performed.
See Full List On Bio-world.com
The technique offers significant savings in time, as chromatography or gel electrophoresis, and the complex blotting procedures for the gel are not required. However, it offers no information on the size of the target protein.[1]
Description Four different sample number, size and style of Hybridisation Manifold are offered; two types of Dot Blotter and two types of Slot Blotter. Typical applications include clone screening with DNA/RNA probes in Southern/Northern blots and immunological screening with antibodies in Western blots. Bio-Rad dot blot apparatus Dot Blot Apparatus, supplied by Bio-Rad, used in various techniques. Bioz Stars score: 99/100, based on 255 PubMed citations. ZERO BIAS - scores, article reviews, protocol conditions and more. Qty: Western Blot Box (11.1 x 5.2 x 4.7cm) bioWORLD’s blot boxes are specially designed western blot boxes to fit blots of any size, including whole blots, half blots, and strips. Whatman ® Minifold ® I 96 well dot-blot array system Minifold I dot-blot system, complete system, 96 well (Acrylic) includes manifold apparatus, 5 x Protran BA85 sheets, 5 x 3 mm Chr sheets, 1/pk Synonym: 96 well dot blot systems, Z613932, complete dot blot system, dot blot systems, dot blotting systems NACRES NB.22. Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations.

Uses[edit]
Performing a dot blot is similar in idea to performing a western blot, with the advantage of faster speed and lower cost.

Dot blots are also performed to screen the binding capabilities of an antibody.[2]
Methods[edit]
A general dot blot protocol involves spotting 1–2 microliters of a samples onto a nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane and letting it air dry. Samples can be in the form of tissue culture supernatants, blood serum, cell extracts, or other preparations.[3]
The membrane is incubated in blocking buffer to prevent non-specific binding. It is then incubated with a primary antibody followed by a detection antibody or a primary antibody conjugated to a detection molecule (commonly HRP or alkaline phosphatase). After antibody binding, the membrane is incubated with a chemiluminescent substrate and imaged.
Apparatus[edit]
Dot blot is conventionally performed on a piece of nitrocellulose membrane or PVDF membrane. After the protein samples are spotted onto the membrane, the membrane is placed in a plastic container and sequentially incubated in blocking buffer, antibody solutions, or rinsing buffer on shaker. Finally, for chemiluminescence imaging, the piece of membrane need to be wrapped in a transparent plastic film filled with enzyme substrate.
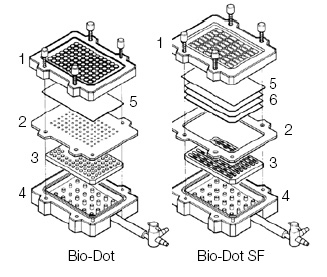
Vacuum-assisted dot blot apparatus has been used to facilitate the rinsing and incubating process by using vacuum to extract the solution from underneath the membrane, which is assembled in between several layers of plates to ensure good seal between sample wells, hold waste solution, and deliver suction force. For chemiluminescence signal detection, apparatus need to be disassembled and the membrane need to be taken out and wrapped in a transparent plastic film.
See also[edit]

References[edit]
- ^'Test Blots, Slot Blots & Dot Blots - Immunodetection Bio-Rad'. Bio-Rad.
- ^Rupprecht, Kevin R.; Nair, Rad K.; Harwick, Larissa C.; Grote, Jonathan; Beligere, Gangamani S.; Rege, Sushil D.; Chen, Yon-Yih; Lin, Zhen; Fishpaugh, Jeffrey R. (15 December 2010). 'Development of a dot-blot assay for screening monoclonal antibodies to low-molecular-mass drugs'. Analytical Biochemistry: 160–164. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2010.08.003. PMID20696124.
- ^'Dot Blot Protocol'(PDF).
Overview
Test blots, as their name implies, are very simple Western blots that are created for the express purpose of optimizing or troubleshooting experimental conditions. They are usually produced by running multiple lanes of the same lysate or purified protein solution on a gel, and after transfer cutting the blot into strips to be tested individually.
Test Blots, Slot Blots & Dot Blots - Immunodetection Bio-Rad
They provide a quick and efficient means of examining a range of antibody dilutions or detection substrates
Dot blots and slot blots are also a very useful variation on the typical Western blot. They do not require gel electrophoresis, so there is no separation of proteins by size.
Instead, the target protein or cell lysate mixture is added directly onto the surface of the nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane. Protein solutions can be applied directly in a small volume, or with a vacuum manifold to produce an orderly grid of samples similar to that seen in Figure 14. Each dot or slot blot would contain known amounts of target protein or cell lysate.
Once dry, dot blots and slot blots are subjected to the same immunodetection steps used for Western blotting, i.e. blocking, antibody incubation, and target detection with substrate. Grey and black spots on the figure below indicate which samples are positive for the target protein and correspond roughly to the bands produced on a Western blot.
Figure 14: Dot Blots and Slot Blots. The dot blots at the left represent a dilution series of a sample, with smaller lighter dots corresponding to lower concentrations of target protein. The slot blots represent a group of random samples, the intensity of the signal corresponds to the concentration of the target protein in that sample.
By making a number of identical dots or slots of a single known protein sample, or a range of sample dilutions, one can quickly test several combinations and concentrations of primary and secondary antibodies. Dot blots and slot blots are also beneficial when screening a large number of samples, or if a simple answer will suffice.
The main downside to slot blots/dot blots is that they provide no information about molecular weight. Thus, it is harder to detect false positive signals, or to tell whether modified forms of a protein are present.
| Detection with Substrate | Chapter 4: Data Analysis |